Columbian Exchange
Written by: Mark Christensen, Assumption College
By the end of this section, you will:
- Explain causes of the Columbian Exchange and its effect on Europe and the Americas during the period after 1492
Suggested Sequencing
This narrative should be assigned to students at the beginning of their study of chapter 1, alongside the First Contacts Narrative.
When European settlers sailed for distant places during the Renaissance, they carried a variety of items, visible and invisible. Upon arriving in the Caribbean in 1492, Christopher Columbus and his crew brought with them several different trading goods. Yet they also carried unseen biological organisms. And so did every European, African, and Native American who wittingly or unwittingly took part in the Columbian Exchange – the transfer of plants, animals, humans, cultures, germs, and ideas between the Americas and the Old World. The result was a biological and ideological mixing unprecedented in the history of the planet, and one that forever shaped the cultures that participated.
For tens of millions of years, the earth’s people and animals developed in relative isolation from one another. Geographic obstacles such as oceans, rainforests, and mountains prevented the interaction of different species of animals and plants and their spread to other regions. The first settlers of the Americas, who probably crossed the Bering Strait’s ice bridge that connected modern-day Russia and Alaska thousands of years ago, brought plants, animals, and germs with them from Eurasia. However, scholars have speculated that the frigid climate of Siberia (the likely origin of the Native Americans) limited the variety of species. And although the Vikings made contact with the Americas around 1000, their impact was limited.
A large variety of new flora and fauna was introduced to the New World and the Old World in the Columbian Exchange. New World crops included maize (corn), chiles, tobacco, white and sweet potatoes, peanuts, tomatoes, papaya, pineapples, squash, pumpkins, and avocados. New World cultures domesticated only a few animals, including some small-dog species, guinea pigs, llamas, and a few species of fowl. Such animals were domesticated largely for their use as food and not as beasts of burden. For their part, Old World inhabitants were busily cultivating onions, lettuce, rye, barley, rice, oats, turnips, olives, pears, peaches, citrus fruits, sugarcane, and wheat. They too domesticated animals for their use as food, including pigs, sheep, cattle, fowl, and goats. However, cows also served as beasts of burden, along with horses and donkeys. Domesticated dogs were also used for hunting and recreation.
The lack of domesticated animals not only hampered Native Americans development of labor-saving technologies, it also limited their exposure to disease organisms and thus their immunity to illness. Europeans, however, had long been exposed to the various diseases carried by animals, as well as others often shared through living in close quarters in cities, including measles, cholera, bubonic plague, typhoid, influenza, and smallpox.
Europeans had also traveled great distances for centuries and had been introduced to many of the world’s diseases, most notably bubonic plague during the Black Death. They thus gained immunity to most diseases as advances in ship technology enabled them to travel even farther during the Renaissance. The inhabitants of the New World did not have the same travel capabilities and lived on isolated continents where they did not encounter many diseases.
All this changed with Columbus’s first voyage in 1492. When he returned to Spain a year later, Columbus brought with him six Taino natives as well as a few species of birds and plants. The Columbian exchange was underway. On his second voyage, Columbus brought wheat, radishes, melons, and chickpeas to the Caribbean. His travels opened an Atlantic highway between the New and Old Worlds that never closed and only expanded as the exchange of goods increased exponentially year after year. Although Europeans exported their wheat bread, olive oil, and wine in the first years after contact, soon wheat and other goods were being grown in the Americas too. Indeed, wheat remains an important staple in North and South America.
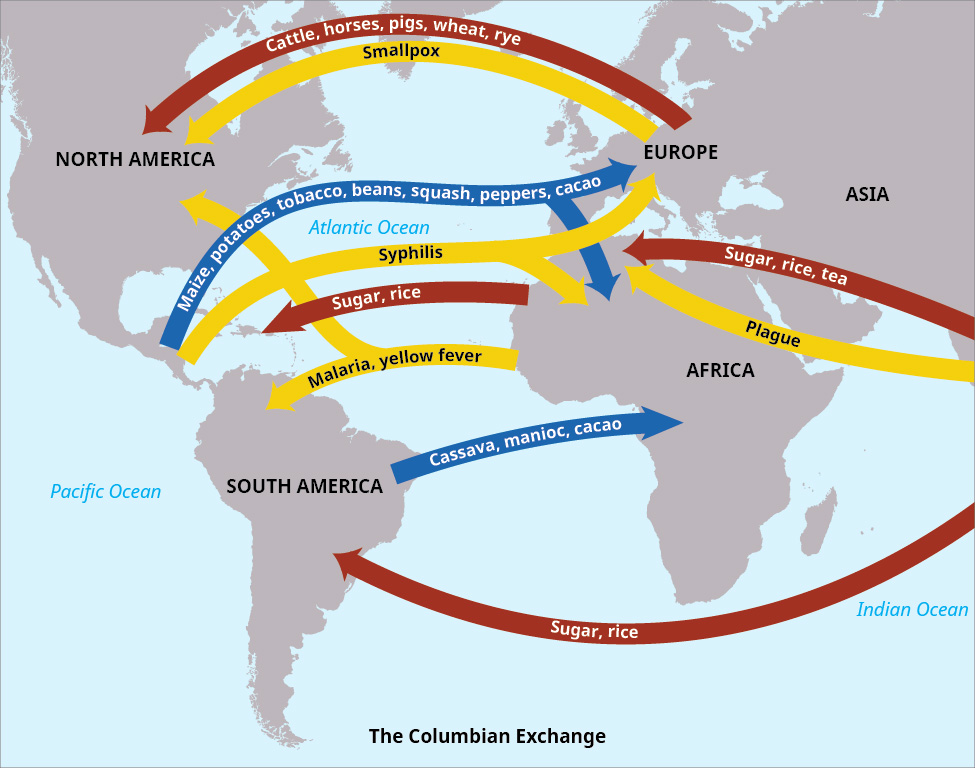
With European exploration and settlement of the New World, goods, animals, and diseases began crossing the Atlantic Ocean in both directions. This “Columbian Exchange” soon had global implications. (attribution: Copyright Rice University, OpenStax, under CC BY 4.0 license)
Horses, cattle, goats, chickens, sheep, and pigs likewise made their New World debut in the early years of contact, to forever shape its landscapes and cultures. On the lusher grasslands of the Americas, imported populations of horses, cattle, and sheep exploded in the absence of natural predators for these animals in the New World. In central Mexico, native farmers who had never needed fences complained about the roaming livestock that frequently damaged their crops. The Mapuche of Chile integrated the horse into their culture so well that they became an insurmountable force opposing the Spaniards. The introduction of horses also changed the way Native Americans hunted buffalo on the Great Plains and made them formidable warriors against other tribes.
The Atlantic highway was not one way, and certainly the New World influenced the Old World. For example, the higher caloric value of potatoes and corn brought from the Americas improved the diet of peasants throughout Europe, as did squash, pumpkins, and tomatoes. This, is turn, led to a net population increase in Europe. Tobacco helped sustain the economy of the first permanent English colony in Jamestown when smoking was introduced and became wildly popular in Europe. Chocolate also enjoyed widespread popularity throughout Europe, where elites frequently enjoyed it served hot as a beverage. A few diseases were also shared with Europeans, including bacterial infections such as syphilis, which Spanish troops from the New World spread across European populations when their nation went to war in Italy and elsewhere.
By contrast, Old World diseases wreaked havoc on native populations. Aztec drawings known as codices show Native Americans dying from the telltale symptoms of smallpox. With no previous exposure and no immunities, the Native American population probably declined by as much as 90 percent in the 150 years after Columbus’s first voyage. The Spanish and other Europeans had no way of knowing they carried deadly microbes with them, but diseases such as measles, influenza, typhus, malaria, diphtheria, whooping cough, and, above all, smallpox were perhaps the most destructive force in the conquest of the New World.
Contact and conquest also led to the blending of ideas and culture. European priests and friars preached Christianity to the Native Americans, who in turn adopted and adapted its beliefs. For instance, the Catholic celebration of All Souls and All Saints Day was blended with an Aztec festival honoring the dead; the resulting Day of the Dead festivities combined elements of Spanish Catholicism and Native American beliefs to create something new. The influence of Christianity was long-lasting; Latin America became overwhelmingly Roman Catholic.
People also blended in this Columbian Exchange. The Europeans, Native Americans, and Africans in the New World procreated, resulting in offspring of mixed race.

Races in the Spanish colonies were separated by legal and social restrictions. In the mid-eighteenth century, casta paintings such as these showed the popular fascination with categorizing individuals of mixed ethnicities.
Throughout the colonial period, native cultures influenced Spanish settlers, producing amestizo identity. Mestizos took pride in both their pre-Columbian and their Spanish heritage and created images such as the Virgin of Guadalupe – a brown-skinned, Latin American Mary who differed from her lighter-skinned European predecessors. The Virgin of Guadalupe became the patron saint of the Americas and the most popular among Catholic saints in general. Above all, she remains an enduring example and evidence of the Columbian Exchange.
Watch this BRI Homework Help video on the Columbian Exchange for a review of the main ideas in this essay.
Review Questions
1. The global transfer of plants, animals, disease, and food between the Eastern and Western hemispheres during the colonization of the Americas is called the
- Middle Passage
- Columbian Exchange
- Triangular Trade
- Interhemisphere Exchange
2. Which of the following provides evidence of the cultural blending that occurred as a result of the Columbian Exchange?
- The adoption of Aztec holidays into Spanish Catholicism
- The willingness of the Spanish to learn native languages
- The refusal of the Aztecs to adopt Christianity
- Spanish priests’ encouragement to worship the Virgin of Guadalupe
3. Which item originated in the New World?
- Sugar
- Smallpox
- Horses
- Potato
4. How did the Columbian Exchange affect Europe?
- Domesticated animals from the New World greatly improved the productivity of European farms.
- Europeans suffered massive causalities form New World diseases such as syphilis.
- The higher caloric value of potatoes and corn improved the European diet.
- Domesticated animals from the New World wreaked havoc in Europe, where they had no natural predators.
5. How did the Columbian Exchange affect the Americas?
- Domesticated animals from the Old World greatly improved the productivity of Native Americans’ farms.
- Native Americans suffered massive causalities from Old World diseases such as smallpox.
- The higher caloric value of crops such as potatoes and corn improved Native Americans’ diets.
- Native Americans learned to domesticate animals thanks to interactions with Europeans.
6. Which item originated in the Old World?
- Sugarcane
- Pumpkins
- Corn
- Potato
Free Response Questions
- Compare the effects of the Columbian Exchange on North America and Europe.
- Explain why historian Alfred Crosby has described the Columbian Exchange as “Ecological imperialism.”
AP Practice Questions
“The Columbian Exchange has included man, and he has changed the Old and New Worlds sometimes inadvertently, sometimes intentionally, often brutally. It is possible that he and the plants and animals he brings with him have caused the extinction of more species of life forms in the last four hundred years than the usual processes of evolution might kill off in a million. . . . The Columbian Exchange has left us with not a richer but a more impoverished genetic pool. We, all of the life on this planet, are the less for Columbus, and the impoverishment will increase.”
Alfred Crosby, The Columbian Exchange: Biological and Cultural Consequences of 1492
Refer to the excerpt provided.1. Which of the following most directly supports Crosby’s argument?
- Population gain in Europe due to New World crops such as the potato
- Population decline in North America due to diseases such as smallpox
- Mass migration of Europeans to North America in the sixteenth century, displacing Native American groups
- Overgrazing by animals introduced by Europeans
2. A historian seeking to discredit Crosby’s argument might use what evidence?
- The immediate and widespread adoption of Christianity in the New World
- Native Americans’ struggles with Europeans for dominance in the New World
- Native American groups’ failed adoption of European technologies
- A net population gain over time due to increased availability of high-caloric foods native to the New World
Primary Sources
Bartholomew Gosnold’s Exploration of Cape Cod: http://historymatters.gmu.edu/d/6617
Suggested Resources
Crosby, Alfred W. The Columbian Exchange: Biological and Cultural Consequences of 1492. New York: Praeger, 2003.
Crosby, Alfred W. Ecological Imperialism: The Biological Expansion of Europe, 900-1900. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004.
Mann, Charles C. 1493: Uncovering the New World Columbus Created. New York: Vintage, 2012.
McNeill, William. Plagues and Peoples. New York: Anchor, 1977.
